In our previous article The Ultimate Guide to Hair Loss Treatment, we discussed different hair loss treatment options, including their advantages and disadvantages. Based on this earlier article, we highlighted hair transplant as one of the treatments that help achieve a fuller and natural-looking head of hair. In the current article, we will put follicular unit excision (FUE) and follicular unit transplantation (FUT) side by side in a clear and detailed FUE vs FUT comparison to determine which is the best option for those who opt for a hair transplant.
What is FUT Hair Transplant?
FUT is a type of hair transplant where a surgeon removes a strip of the scalp and microscopically dissects this tissue into 1-3 hair grafts. Then, the surgeon makes incisions on the scalp and transplants the grafts on the bald area before dressing the surgical site in a bandage or gauze for a few days.
Usually, people undergoing a FUT hair transplant do not need to shave their hair on the donor region. In fact, long hair can come in handy in covering the area of the scalp where the surgeon made a strip to harvest hair grafts. Otherwise, the strip will be visible as a scar.
What Is FUE Hair Transplant?
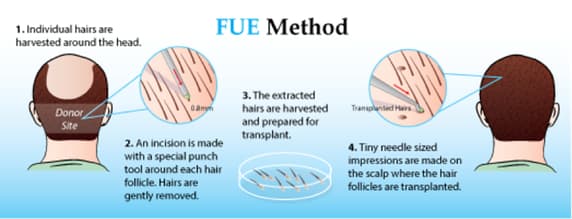
FUE is a type of hair transplant where a surgeon extracts individual follicular units from the donor area. The next step involves preparing the follicles for their eventual transplantation to the bald part of the head.
Usually, the surgeon makes tiny incisions on the bald scalp region and inserts the newly harvested follicles. Then, the surgeon covers the surgical site with either a bandage or gauze. One should remove this hair transplant dressing after 2-3 days.
Scab formation often occurs a few hours after an FUE procedure. Usually, the scabs fall off within one week. However, they sometimes take longer. The new hair grafts might take just over a week and up to 14 days before they become secure.
How Has FUE Transplant Evolved Over Time?
If you want to undergo a hair transplant, the doctor will likely provide you with a choice between FUE and FUT because these are the most popular hair transplant procedures. A strong debate has emerged in recent times as the demand for FUE continues to increase due to significant improvements in this procedure.
A while back, FUT was the gold standard in the hair transplant field. At the time, FUE was still in its infancy. Very few hair transplant surgeons also performed this procedure. Most of these experts struggled with poor survival rates and higher transection rates.
Today, there are more surgeons skilled in the FUE procedure and transection rates have improved. The rate of survival of FUE grafts is within the same range as FUT grafts.
Forceps trauma is also not a concern because extracting tethered grafts is gentler. Consequently, these improvements have raised questions about whether FUE is better than FUT.
What Makes FUE Better than FUT?
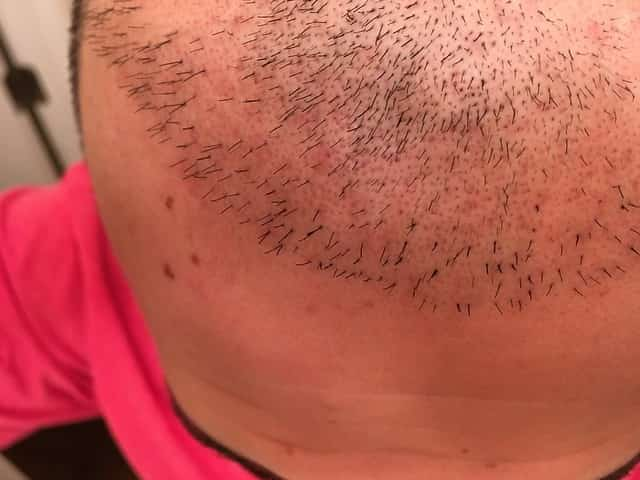
FUE is better than FUT because it does not lead to visible scars. FUT hair transplant is different and usually causes a linear scar whenever a surgeon removes a strip of the scalp.
FUE is also better or ideal for people who like to maintain short hair. Otherwise, choosing FUT will leave you with a visible scar on the donor part of the scalp.
In addition, FUE is less painful than FUT. Individuals undergoing FUE often have minimal pain a day after the procedure. However, FUT causes more pain because the surgeon must suture or close down the wound or source of hair grafts (strip).
FUE further leads to faster recovery than FUT because no stitching is done with this hair transplant method. With FUT, recovery takes longer because the wounds on the scalp that require more time to heal. FUE is also a better choice for individuals with poor scalp laxity (the ability of the scalp to stretch when tension is applied).
Today, the neograft method, a semi-automated type of FUE allows surgeons to extract hair follicles at a faster rate. It also significantly increases the success of this procedure, leads to less discomfort, and reduces trauma to the scalp.
The success rate of FUE and FUT is comparable, often over 90%. However, neograft achieves a relatively higher success rate, which can, in some cases, go as high as 100%.
What Makes FUT Better than FUE?
FUT is better than FUE for patients with extensive balding because it yields more hair grafts for subsequent transplantation. It also leads to a fuller head of hair or a more natural and denser coverage.
FUT is also cheaper than FUE because the surgeon does not extract individual hair follicles but rather dissects the scalp tissue (strip) into one or more hair grafts. As a result, FUT is faster to perform than FUE. It is also less tedious or labor intensive than the FUE hair transplant method.
In addition, FUT is an ideal hair transplant method for people who prefer long hair because they do not need to shave the donor area to proceed with the procedure.
With FUE, one must shave their hair to allow the surgeon to extract individual hair follicles for transplantation.
FUT can further help harvest longer hair shafts. As a result, a surgeon can identify hair curling, which makes transplanting hair more challenging.
The new long hair FUE can also yield longer hair shafts. However, this surgical technique requires a highly skilled and experienced surgeon.
FUT also requires fewer hair grafting sessions compared to FUE. It follows that a surgeon can transplant more grafts per session in FUT than in FUE.
Based on these insights, there is no ideal or one-size-fits-all choice of hair transplant. Some people may even require combined FUT and FUE hair transplants. Thus, the best method varies depending on individual characteristics and personal preferences. This article will help you understand which hair transplant method best suits you and your needs.