The goal of adopting a particular diet is maintaining or achieving good health and well-being. However, it is hard to know which diet plans to follow safely. Right now, there are many diets being fronted on the internet. They include absurd celebrity, crash, and fad diets.
The safety of these diets is known to a greater extent. However, evidence shows that some of these dietary choices may be unhealthy. For instance, experts have warned that crash diets may cause sudden death if done without proper medical supervision. Some extreme forms of detox diets such as juice fasting or cleansing might also have negative health implications.
Therefore, if you plan on pursuing healthy eating habits, you should only consider adopting highly recommended and doctor-approved diets. Otherwise, you risk unconsciously embracing diet choices with detrimental health effects. You might also end up not achieving your healthy eating goals. In addition, your health will be worse off from where you began.
The Top 5 Doctor-Approved Diets For Good Health
Health-conscious people seem to be in a constant search for better ways to lead healthy life. Dieting significantly contributes to this goal. However, one should pursue physician or doctor-approved diets instead of health trends promising instant results on the internet and other platforms. These recommended diet plans will, without doubt, provide more benefits and pose no health risks. Researchers also try and test these diets extensively before presenting them to the public. This thorough testing guarantees the safety and success of these diet plans in improving health outcomes.
The Mediterranean diet (MedDiet)
The Mediterranean diet is among the most popular and healthiest dietary patterns. Only persons living along the Mediterranean Sea initially consumed this diet. However, people across the world now know it. Scientists have also extensively researched it. As a result, they have found that its main nutritional components contribute to better health.
The Mediterranean diet requires taking fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, whole grains (cereals), fish, extra virgin olive oil, and moderate alcohol (red wine). You can also take dairy products and red meat with this diet but in low quantities. It emphasizes poultry and fish as the main sources of protein. It also discourages processed foods, but you can take them in relatively low amounts.
Olive oil, nuts, and fish provide cardioprotective benefits because they contain omega fatty acids. As a result, they help promote cardiovascular health and prevent heart diseases. Taking red wine also improves lipid metabolism and hemostatic balance. The different nutrients from this diet also help prevent breast cancer, type 2 diabetes, dementia, obesity, hypertension, and depression.
Strict adherence to the Mediterranean diet is necessary to derive sufficient preventative and protective effects. At the same time, moderate consumption of dietary components is always desirable for the best outcomes. This diet lacks a physical activity component. Thus, adding physical exercise can improve its overall efficacy.
Talking to a registered dietitian also provides an added advantage if you want to modify specific risk factors. These health professionals can advise on appropriate food groups and nutrients. It follows that not many recommendations exist to date regarding this diet. However, one study recommended the following quantities:
- Cereals (one to 13 servings)
- Fruits (one-half to two servings)
- Olive oil (up to eight servings)
- Vegetables (three to nine servings)
- Moderate red wine intake (daily)
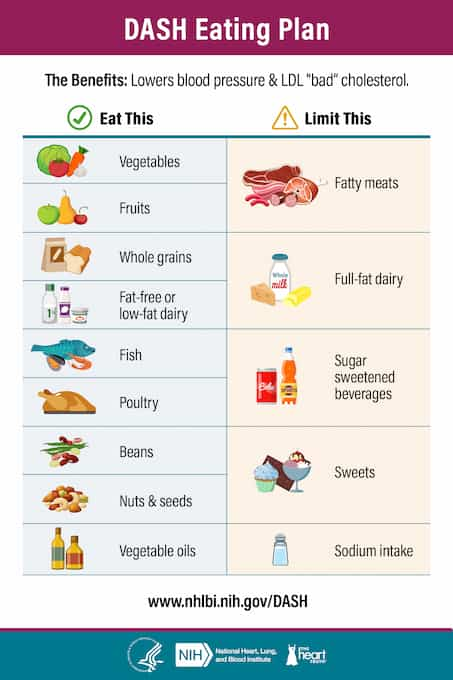
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet
The DASH diet supports a more flexible eating plan. It is not as strict as the Mediterranean diet. It helps combat high blood pressure and improve cholesterol levels. As a result, it keeps the heart healthy and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
The DASH diet is highly recommended for people with hypertension or those at risk of this disease. However, it does not mean you cannot adopt it if you are perfectly healthy. It is safe for everyone, but it seems to work best if you want to keep your heart healthy and regulate your blood pressure.
The DASH diet has been extensively researched. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) funded the studies that led to its adoption. It emphasizes eating fruits, vegetables, fish, nuts, beans, poultry, whole grains, and vegetable oils.
You can also take low-fat/fat-free dairy products with this diet. It also requires you to limit your intake of sugar-sweetened beverages, alcohol, and foods high in saturated fats. In this regard, you should reduce your consumption of palm, coconut, and palm kernel oils because they have a lot of saturated fatty acids.
The DASH diet targets 2,000 calories daily. However, calorie intake may be higher or lower depending on your age, medical conditions, sex, the purpose of adopting this diet, and activity level. You should take foods low in sodium (salt). In addition, you should consume foods rich in fiber, potassium, calcium, protein, and magnesium. If you have kidney disease, you should limit your potassium intake.
If you plan to lose weight, you should eat more non-starchy fruits and vegetables. The DASH diet also has a physical activity component. It recommends exercising for at least 30 minutes daily or 2 hrs 30 min weekly. If struggling with weight, you should exercise for 60 minutes daily.
The MIND diet
The Mediterranean-Dash Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) diet is an eating pattern that combines specific components of the Mediterranean and DASH diets. It puts together brain-healthy food groups from these diets and uses them to prevent neurocognitive disorders.
These foods help improve cognition and slow neurodegeneration. As a result, the MIND diet reduces the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Specifically, it lowers this risk by up to 53 percent for people who strictly adhere to this diet and about 35 percent for those who moderately follow it.
It is easier to follow than the Mediterranean diet. It includes ten dietary components comprising whole grains, green leafy vegetables, olive oil, berries, nuts, poultry, fish, beans, wine, and other vegetables. In addition, it discourages the intake of cheese, fast/fried foods, red meat, sweets, butter, pastries, and stick margarine.
Usually, the MIND diet does not recommend all fruits. It only requires you to eat berries. Blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, and strawberries are very good at improving cognitive function. They contain potent antioxidants that help protect the brain.
The MIND diet does not offer physical exercise recommendations. However, adding a physical exercise component can help boost brain health for people at risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
The Flexitarian diet
The flexitarian diet is a semi-vegetarian diet. It is basically a vegetarian with occasional meat or fish intake. Dawn Jackson Blatner, an American dietician, created this diet in 2008. Flexitarian is a blend word for “flexible” and “vegetarian.”
The flexitarian diet is among the best diets overall. It is fit for people who do not want to follow a strictly vegetarian diet. It is also appropriate for meat reducers (people who want to keep their meat intake at a minimum). Usually, it requires consuming fruits, vegetables, nuts/seeds, whole grains, meat, and fish.
It is a more sustainable diet plan. It also enables vegetarians to add adequate proteins to their diet. In addition, it is well balanced and supports weight loss. It is very flexible, requires home cooking, and provides a lot of tasty recipes. However, it allows occasional eating out.
The flexitarian diet generally leaves you feeling fuller and helps maintain a healthy weight. It also provides other benefits. In particular, it lowers cholesterol levels, improves blood pressure regulation, and controls blood sugars levels. In addition, it reduces the risk of coronary diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
The Ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet is popularly known as the keto diet. Most people today use it as a remedy for weight loss. However, it is known in medical circles as an effective treatment for epilepsy. Evidence shows that the keto diet significantly reduces epileptic seizures in children and young people. It requires high fat, moderate protein, and low carbohydrate intake.
Under normal circumstances, the body uses carbohydrates as a primary energy source. However, taking carbohydrates in relatively low quantities in a keto diet forces the body to burn fats in its place. This diet is highly effective in managing epilepsy. In addition, it facilitates weight loss, at least in the short term. Despite these benefits, the keto diet is likely to cause new problems.
For instance, the keto diet might increase cholesterol levels and contribute to hyperlipidemia if not done right. This concern has resulted in a shift towards polyunsaturated fats, which lead to a healthier lipid profile. It also increases the risk of kidney stones, constipation, and hypoglycemia.
The keto diet is unsustainable in the long run. Under normal circumstances, maintaining an adequate supply of fats to fuel ketosis requires the frequent intake of dairy fats, nuts, and meat. These foods can make this diet very expensive to sustain.
Factors to Consider When Adopting a New Diet
Usually, new diet plans fail because we do not consider certain aspects. This problem raises questions about the specific factors one should think of before adopting a new diet.
Cost/affordability
Cost is a significant determinant of how well one can adhere to a particular diet plan. Therefore, you should always consider if you can comfortably and consistently buy the various food items identified as the cornerstone of a new diet. Otherwise, you might start the diet and abandon it shortly due to cost implications. You should self-evaluate to ensure whichever diet you adopt is successful and helps you achieve your health goals.
Sustainability
In addition, you should consider whether your target diet is sustainable or not. For instance, it is easier to sustain a plant-based diet in the long run because it is cheaper and readily available. However, adhering to a diet requiring lots of meat and dairy products, such as the keto diet, is challenging, at least for most people.
Availability
You should also assess the food items included in a new diet and ascertain that you can access them as regularly as needed. Otherwise, you might choose a diet plan only to realize later that you cannot get a consistent supply of one or more food items. Therefore, select a dietary pattern you can work with comfortably using locally available food items.

